title: “了解CDN” tags: [] slug: 3d406863 date: 2021-04-17 23:21:15 summary: “本文介绍了解CDN,包括使用场景、实现细节等,以提高了解CDN的效率。”
We use CDNs to improve web performance — but do you really understand how they work? Here’s a quick primer.
Concept
内容分发网络(英语:Content Delivery Network或Content Distribution Network,缩写:CDN)是指一种透过互联网互相连接的电脑网络系统,利用最靠近每位用户的服务器,更快、更可靠地将音乐、图片、视频、应用程序及其他文件发送给用户,来提供高性能、可扩展性及低成本的网络内容传递给用户。
That’s from Wikipedia as a basic definition. Next, the implementation.
How it works
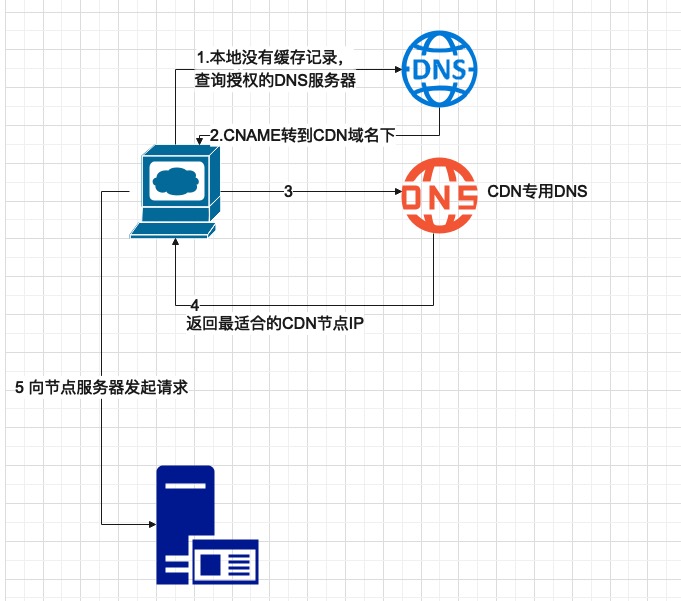
From the diagram, the key building blocks are:
CNAME: you configure a custom domain that CNAMEs to the CDN’s domain.- CDN‑managed
DNS: needed to resolve domains to IPs. - Global load balancing (
GSLB): instead of static DNS → IP, responses are dynamic, returning the best edge IP so users connect to a nearby node.
OK,那么这样,CDN就理解了。
DNS‑prefetch
DNS resolution costs time. To speed things up, you can pre‑resolve cross‑origin static domains. Chrome uses dedicated threads for DNS prefetching.
普遍来说合理的dns prefetching能对页面性能带来50ms ~ 300ms的提升,有人做了这方面的统计
<link rel="dns-prefetch" href="//static.1991421.cn">
Benefits
CDNs improve resource delivery speed and can also save bandwidth. Third‑party CDN resources are often cached across sites, reducing redundant downloads.
Final Thoughts
Knowing both the what and the why helps you wield the tech better.

